
by Chiara Bassi | Mar 9, 2015
Bottles and Bottling Bottling . is the last stage of wine production and must guarantee maximum stability. In order to avoid contact with the air and consequent problems of oxidation and browning, fillers are used...
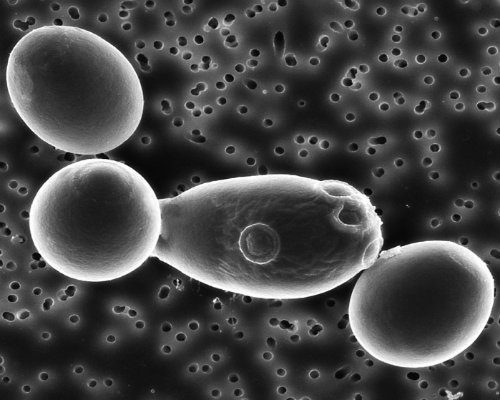
by Chiara Bassi | Mar 9, 2015
Alcoholic Fermentation Alcoholic fermentation is carried out by Saccharomyces yeasts that transform sugars, particularly glucose, into ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide and heat energy. The ethyl alcohol that forms and is actually present in wine...

by Chiara Bassi | Mar 9, 2015
White vinification In fermentation, there is no contact between must and marc. Since the colour pigments are located in the skins, it is sufficient to remove them from the must to obtain a white wine even from black grapes. Harvest and transport...

by Chiara Bassi | Mar 8, 2015
Winemaking in Red PRESSING / DE-stemming = must always be soft to avoid excessive tannin extraction, which is why de-stemming is increasingly carried out at the same time or before crushing. The removal of the stalks...

by Chiara Bassi | Mar 8, 2015
Must The decision to harvest comes after several analytical and instrumental controls that allow us to precisely and rigorously follow the evolution of the concentration of sugars, acids, polyphenols and aromas, until we identify the moment...

by Chiara Bassi | Mar 8, 2015
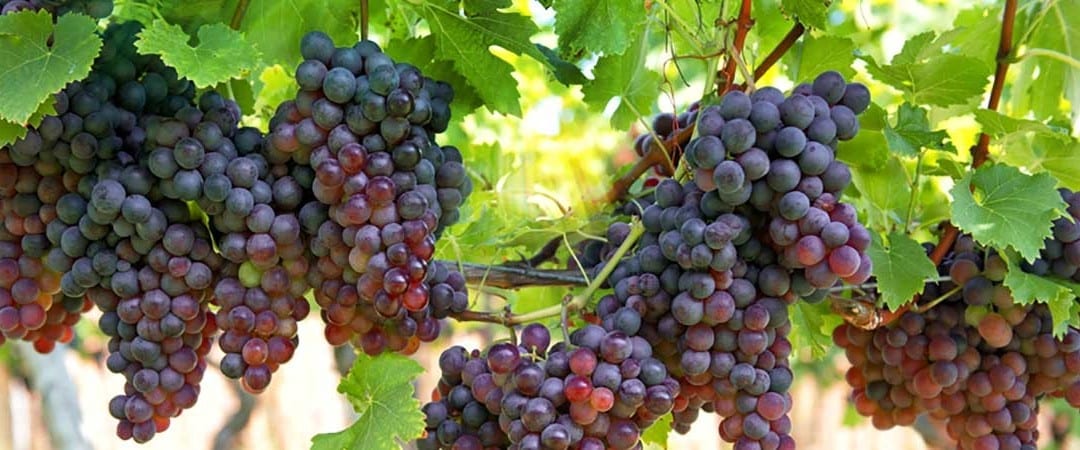
Grape Cluster The clusters may be more or less voluminous, tight or sparse, winged or half-winged, but they always consist of grapes. They are set on a small branch called a stalk or rachis that accounts for 3-5% of their weight. Rich in lignin and cellulose, the...







